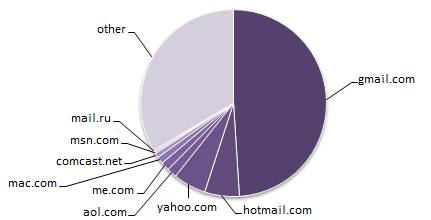
A whopping 49% of Artsy users have “gmail.com” email addresses. The next domain name, “hotmail.com”, doesn’t even come close, with only 6%.
GMail addresses ignore periods and are case-insensitive. For example, “Donald.Duck@gmail.com” and “donaldduck@gmail.com” are the same account. You can log-in to GMail with both. Users often register with the former and try to log-in to Artsy with the latter. With so many GMail users, expect a dozen support emails per day.
The solution is to normalize these emails into a canonical form.
We use our newly open-sourced gem called canonical-emails. It patches Mail::Address methods at runtime.
module CanonicalEmails
module GMail
def self.transform(value)
Mail::Address.new(value).tap do |email|
if email.domain && [ "gmail.com" ].include?(email.domain.downcase)
email.instance_eval do
def get_local
value = super
value.gsub(".", "").downcase if value
end
def domain
value = super
value.downcase if value
end
end
end if value
end
end
end
end
It would be great to see contributions to our gem if you have knowledge of special handling with other email providers!
On the application side, Artsy stores both the original email address entered by the user and the canonical representation and perform all lookups by the canonical value.
class User
include Mongoid::Document
include CanonicalEmail::Extensions
field :email, type: String
field :lookup_email, type: String
before_save :update_lookup_email
canonical_email :email, CanonicalEmails::GMail, CanonicalEmails::Downcase
def self.find_by_email(email)
email = CanonicalEmails::GMail.transform(email).to_s
email = CanonicalEmails::Downcase.transform(email).address
first(lookup_email: email)
end
private
def update_lookup_email
self.lookup_email = self.canonical_email
end
end
What is your email domain breakdown? Here’s the MongoDB/Mongoid/ruby map/reduce that I used to get the graph above.
map = %Q{
function() {
emit((this.email).split("@")[1], { count: 1 });
}
}
reduce = %Q{
function(key, values) {
var result = { count: 0 };
values.forEach(function(value) {
result.count += value.count;
});
return result;
}
}
User.all.map_reduce(map, reduce)
.out(inline: true)
.sort_by{ |v| -v["value"]["count"] }
.take(10)
.map { |v| { v["_id"] => v["value"]["count"] / User.count }}
Raw output for our top 10.
[
{ "gmail.com" => 0.49 },
{ "hotmail.com" => 0.06 },
{ "yahoo.com" => 0.057 },
{ "aol.com" => 0.017 },
{ "me.com" => 0.015 },
{ "mac.com" => 0.012 },
{ "comcast.net" => 0.008 },
{ "msn.com" => 0.003 },
{ "mail.ru" => 0.003 },
{ "verizon.net" => 0.003 }
]
Comments